Statistical releases provide a summary of the most recent values and trends for the published statistical indicators series compiled by the Croatian National Bank.
Statistics
- Release calendar
- Statistical releases
- Indicators of banking system operations
- Main macroeconomic indicators
-
Statistical data
-
Financial sector
- Republic of Croatia contribution to euro area monetary aggregates
- Consolidated balance sheet of MFIs
- Central bank (CNB)
- Other monetary financial institutions
- Other financial corporations
- General government sector
- External sector
- Financial accounts
- Securities
- Selected non-financial statistics
- Payment systems
- Payment services
- Currency
- Turnover of authorised exchange offices
- Archive
-
Financial sector
- SDDS
- Regulations
- Information for reporting entities
- Information for users of statistical data
- Use of confidential statistical data of the CNB for scientific purposes
- Statistical surveys
- Experimental statistics
Statistical releases
General government debt statistics for September 2021
According to final data, the total consolidated debt of all general government sub-sectors[1] reached HRK 344.7bn at the end of September 2021, up HRK 3.9bn (or 1.1%) since the end of June 2021 and up by HRK 18.7bn (or 5.7%) since the end of September 2020. The annual debt growth was due to an increase in the domestic debt by HRK 7.9bn (or 3.6%) and in the external debt by HRK 10.8bn (or 10.2%). Domestic debt grew by HRK 6.3bn (or 2.9%), while external debt shrunk by HRK 2.5bn (or 2.1%) from the last quarter.
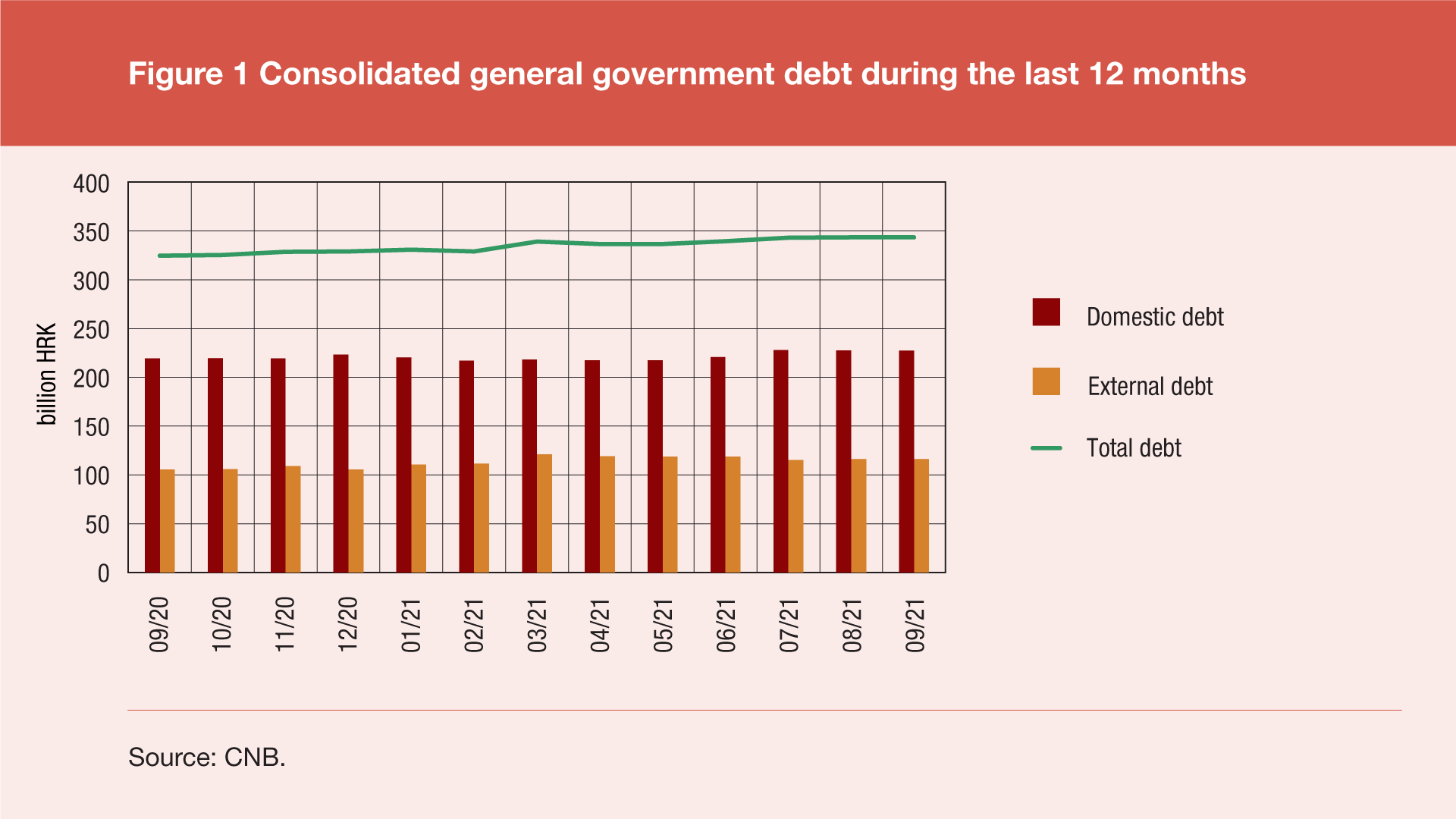
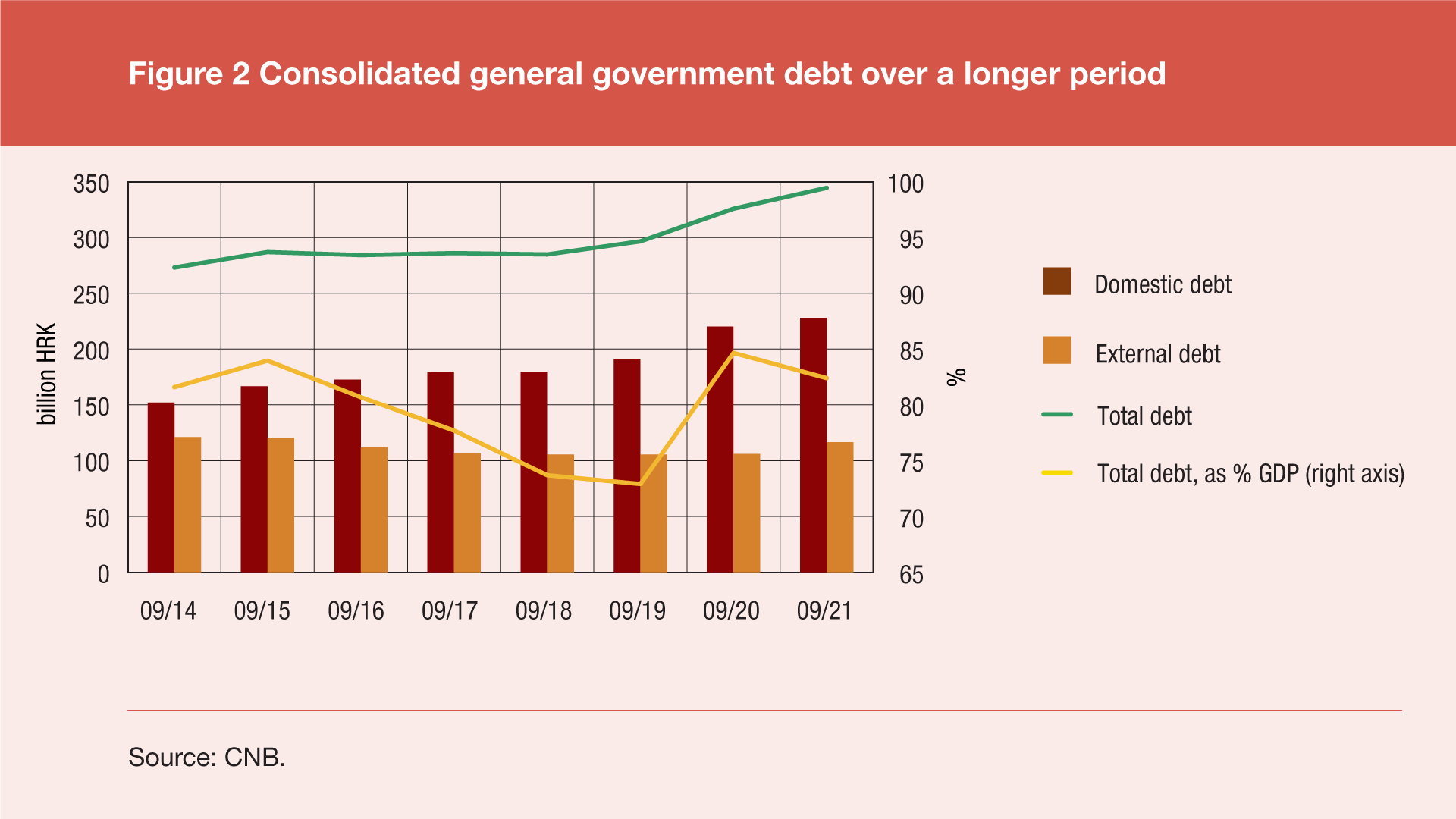
Measured against the annual GDP[2], the total debt amounted to 82.4% of GDP at the end of eptember 2021, and 84.7% of GDP at the end of September 2020, which is a decrease of 2.3 percentage points on an annual level, but also a decrease of 3.7 percentage points over previous quarter, when this share was 86.1%.
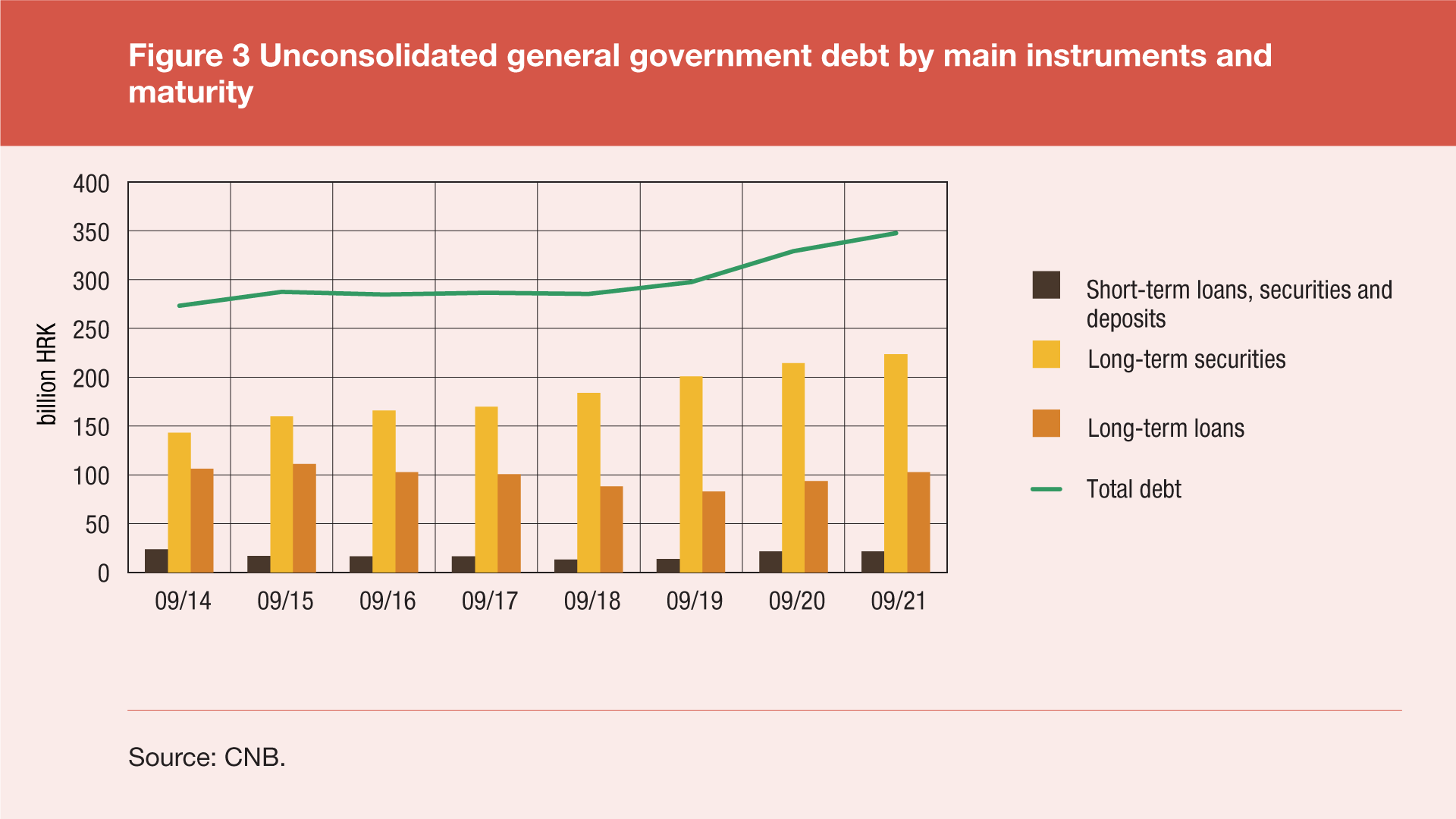
Data on the structure of general government debt by main debt instruments and maturity is available only for general government unconsolidated debt[3]. Long-term debt instruments dominate the structure of this debt: at the end of September 2021, most of the debt was made up of bonds (64.3%), the second by importance were long-term loans (29.5%), and last were short-term loans, securities and deposits (jointly 6.2%). Short-term debt was higher by HRK 0.2bn (or 0.8%) at the end of September 2021 from end-September 2020, while long-term debt increased by HRK 18.2bn (or 5.9%) in the same period.
Statistical time series: Table I3 General government debt (ESA 2010)
-
This debt excludes the cross claims of institutional units within the same sub-sector and between sub-sectors, the so-called Maastricht debt. ↑
-
Calculated as the sum of the preceding four quarterly GDP figures. ↑
-
The unconsolidated debt represents the Maastricht debt increased by cross claims of different units within the general government sector. ↑
